The Remarkable World of Aquatic Snails: Nature's Unsung Aquarium Heroes
Dive into the fascinating realm of aquatic snails, the often-overlooked stars of freshwater ecosystems. These tiny mollusks play a crucial role in maintaining water quality and biodiversity, both in natural habitats and home aquariums. From their unique evolutionary adaptations to their surprising intelligence, aquatic snails offer a captivating glimpse into the intricate balance of underwater life.
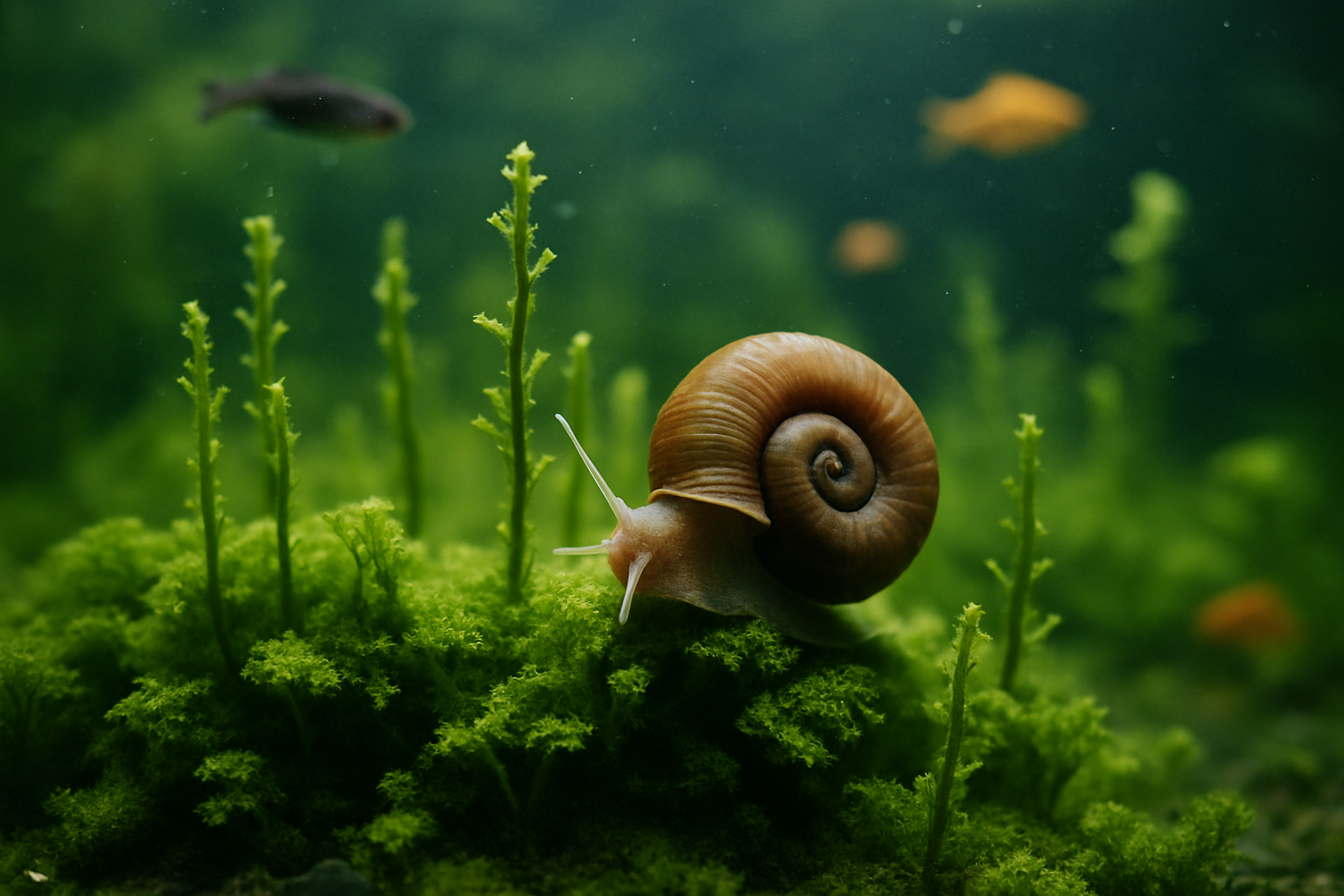

The Evolutionary Journey of Aquatic Snails
Aquatic snails have a rich evolutionary history dating back over 500 million years. These resilient creatures have adapted to a wide range of freshwater environments, from fast-flowing streams to stagnant ponds. Over time, they have developed specialized features to thrive in underwater habitats, including gills for respiration and protective shells that serve as both armor and buoyancy control.
The diversity of aquatic snail species is truly astounding, with over 4,000 known freshwater species worldwide. This remarkable variety is a testament to their adaptive capabilities and the different niches they occupy in aquatic ecosystems. From the common pond snail to the exotic ramshorn, each species has its own unique characteristics and ecological role.
Aquatic Snails as Nature’s Cleanup Crew
One of the most valuable contributions of aquatic snails is their role as natural water purifiers. These diligent creatures act as living filtration systems, constantly grazing on algae, decaying plant matter, and other organic debris. By consuming these materials, snails help to maintain water clarity and prevent the buildup of harmful substances that can negatively impact aquatic life.
In home aquariums, aquatic snails have gained popularity among enthusiasts for their ability to keep tanks clean and algae-free. Many species, such as the nerite snail, are prized for their voracious appetite for algae and their gentle nature towards other tank inhabitants. This natural cleaning service can significantly reduce the maintenance required for aquarium upkeep, making snails an attractive option for both novice and experienced aquarists.
The Secret Intelligence of Aquatic Snails
Contrary to popular belief, aquatic snails possess a surprising level of intelligence and sensory capabilities. Recent studies have revealed that these creatures can learn from experience, form memories, and even exhibit problem-solving behaviors. For example, some species of aquatic snails have been observed using tools to defend themselves against predators, showcasing a level of cognitive ability previously unrecognized in these animals.
Furthermore, aquatic snails possess a complex sensory system that allows them to navigate their underwater world with remarkable precision. They use chemoreception to detect food sources and potential mates, and some species even have primitive eyes that can distinguish between light and dark. This sophisticated sensory array enables snails to thrive in diverse aquatic environments and adapt to changing conditions.
The Ecological Impact of Aquatic Snails
Beyond their role as water purifiers, aquatic snails play a crucial part in the broader ecosystem. They serve as a food source for various predators, including fish, birds, and mammals, forming an essential link in the aquatic food chain. Additionally, snails contribute to nutrient cycling by breaking down organic matter and releasing essential nutrients back into the water.
In some cases, aquatic snails can also act as indicators of environmental health. Certain species are particularly sensitive to changes in water quality, making them valuable bioindicators for scientists and conservationists. By monitoring snail populations and behavior, researchers can gain insights into the overall health of aquatic ecosystems and detect potential environmental threats.
Challenges Facing Aquatic Snail Populations
Despite their resilience and adaptability, aquatic snail populations face numerous threats in today’s changing world. Habitat loss, pollution, and climate change all pose significant challenges to these important creatures. In many areas, the introduction of invasive species has disrupted native snail populations, leading to declines in biodiversity and ecosystem stability.
Conservation efforts are underway to protect vulnerable aquatic snail species and their habitats. These initiatives focus on preserving water quality, restoring degraded ecosystems, and educating the public about the importance of these often-overlooked animals. By raising awareness and implementing targeted conservation strategies, researchers and environmentalists hope to ensure the long-term survival of aquatic snails and the ecosystems they support.
The Future of Aquatic Snail Research and Conservation
As our understanding of aquatic snails continues to grow, so too does the potential for groundbreaking discoveries and innovative conservation approaches. Scientists are exploring the use of aquatic snails in bioremediation, harnessing their natural filtration abilities to clean polluted water bodies. This promising field of research could lead to more sustainable and eco-friendly water treatment solutions in the future.
Additionally, the study of aquatic snail biology and behavior is opening up new avenues in fields such as neuroscience and evolutionary biology. By unraveling the mysteries of snail intelligence and adaptation, researchers hope to gain insights that could have far-reaching implications for our understanding of cognitive development and environmental adaptation across species.
In conclusion, the world of aquatic snails is a treasure trove of surprises and untapped potential. From their vital ecological roles to their unexpected intelligence, these small but mighty creatures continue to captivate scientists and nature enthusiasts alike. As we delve deeper into their underwater realm, we gain not only a greater appreciation for these unsung heroes of aquatic ecosystems but also valuable lessons in resilience, adaptation, and the intricate balance of nature. By protecting and studying aquatic snails, we invest in the health and diversity of our planet’s precious water resources for generations to come.